Data Types (Numbers, String, Boolean)
Numbers
A number can be of any value that is positive, negative or in decimals.
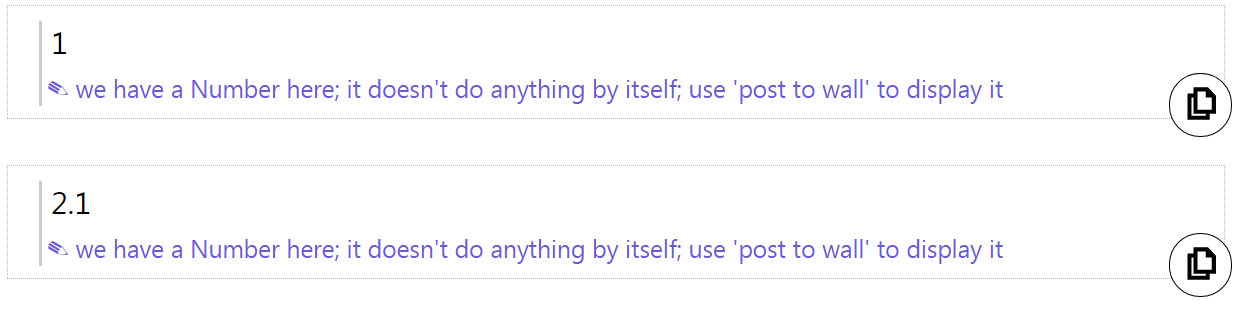
In the example above, we have a positive number, 1, and a positive decimal number, 2.1
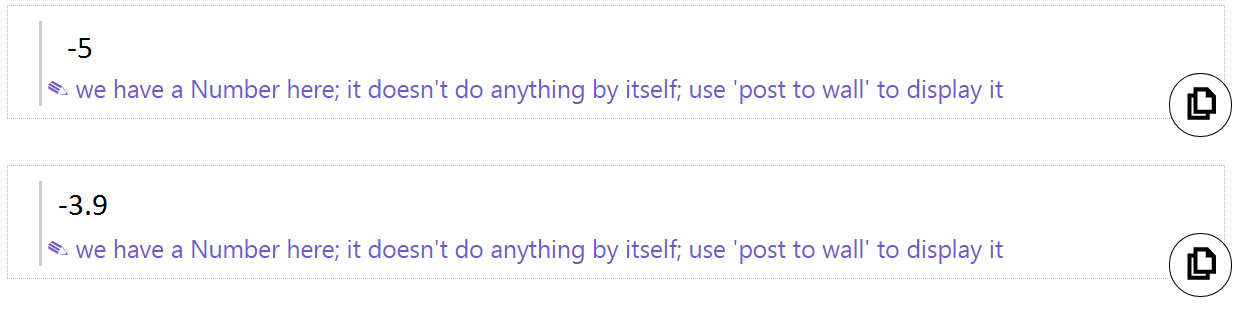
In the example above, we have a negative number, -5, and a negative decimal number, -3.9

In the example above, we can perform different action with numbers such as addition, subtraction, division or comparison.
Strings
Strings are pieces of text within the " "

In the example above,
- We have a string text of "this is a string" that is saved in a variable called 's'.
- We can also concatenate (add) two or more strings together using the " || " operator
- We can also count the length of the string using the "count" action. (Note that spaces are included in the count value too!)
Booleans (True or False)
Booleans are "True" or "False"

In the example above, we declared a variable and assign the boolean value of "True" to 't' and "False" to 'f'
Not Operator
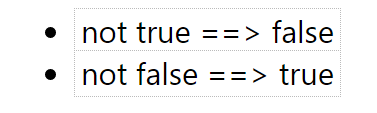
We can convert a boolean from "True" to "False" using the "NOT" operator and vice versa!
And Operator

In the example above, we use the "AND" operator which takes two boolean and return a boolean. AS A RULE OF THUMB, IF ANY OF THE BOOLEAN HAS A "FALSE", THE RESULT WILL AUTOMATICALLY BE "FALSE", THE RESULT WILL ONLY BE "TRUE" WHEN THE TWO BOOLEANS ARE "TRUE".
Or Operator

IN THE EXAMPLE ABOVE, WE USE THE "OR" OPERATOR WHICH TAKES TWO BOOLEAN AND RETURN A BOOLEAN. AS A RULE OF THUMB, IF ANY OF THE BOOLEAN HAS A "TRUE", THE RESULT WILL AUTOMATICALLY BE "TRUE" AS WELL, THE RESULT WILL ONLY BE "FALSE" WHEN BOTH BOOLEANS ARE "FALSE
Conclusion
- There are three basic data types, Number, String and Boolean!
- These three data types are most commonly used in programming!
- There are lots of different actions that you can apply to each data type! Explore it on your own!