Implementation
Home → Implementation
PRIDAR Chatbot Implementation
User Authentication and Login

Sendgrid was used as part of the authentication system to e-mail the users for verification.
APIs, Tools and Dependencies

Retrieve and update user account details and update user scores.

Used to retrieve information regarding PRIDAR standard as well as posting user queries.

Deployment of the chatbot
Data Visualisation
Quickchart is the API used to generate visualisations of user data
Implementation Overview
Key Features
Voiceflow implementation overview:
Voiceflow allows developers to design a diagram flowchart for conversations between the user and the chatbot. At each step in the flowchart either a response in the form of texts or choices is sent or customised javascript code can be executed to assist the functionalities of the chatbot as well as being able to make API calls to exchange data with external services.
User Login and Authentication System
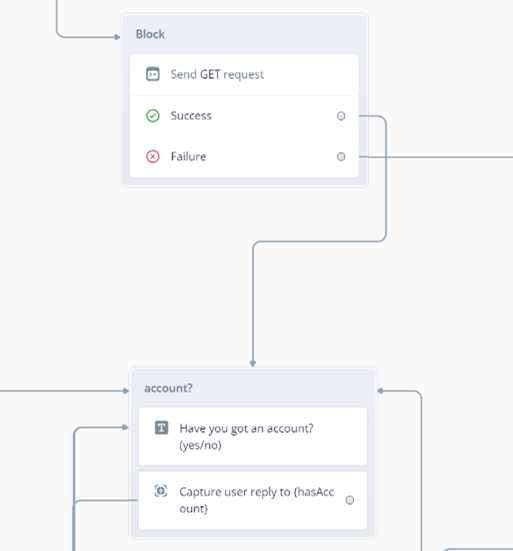
1. Upon launching, credentials of all users are extracted from the Airtable database using its API, then users are asked whether they have an account or not, if they do then they are asked to register for an account.
2. Registering for an account requires the user to enter an account name and password. The account name is checked against the existing credentials using a sequential search to make sure it is not in use, an email address is also prompted for password recovery.
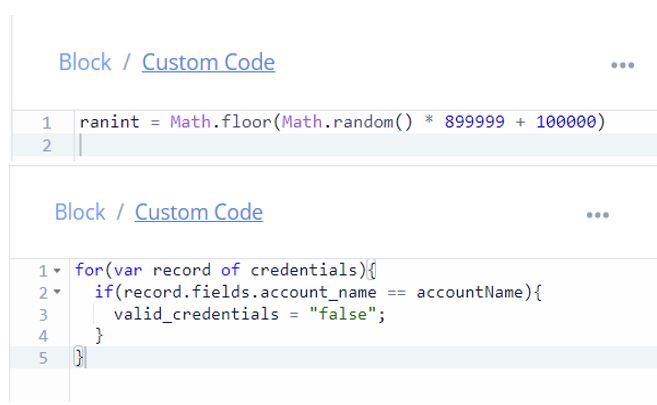
The email is verified by generating a random 6 digit number and having it sent to the email address using Sendgrid, The user is prompted to enter the 6 digit code and only if the code matched is the account name, password and email stored in the database using Airtable’s API.
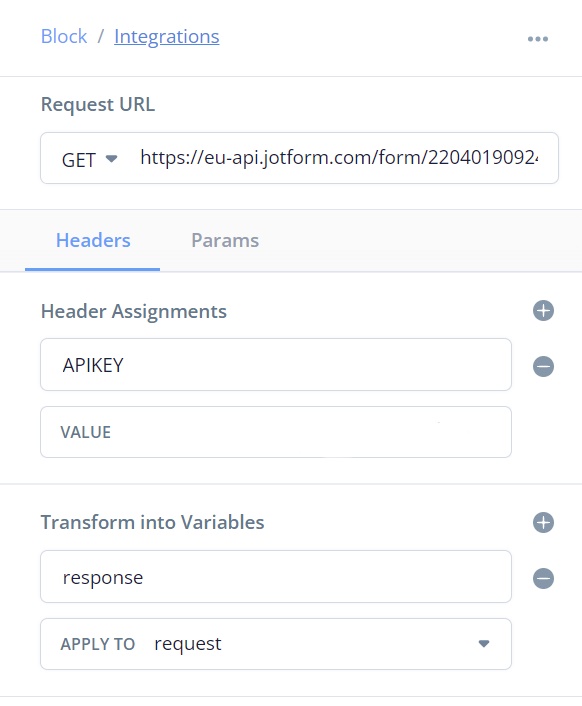
3. Logging in requires the user to enter their account name and password, if the account name does not exist in the database or if the password does not match the account name, users are prompted whether they have an account again.
 4. Upon successful completion of either log in or sign up users are then prompted the main menu.
4. Upon successful completion of either log in or sign up users are then prompted the main menu.
Test Knowledge implementation overview:
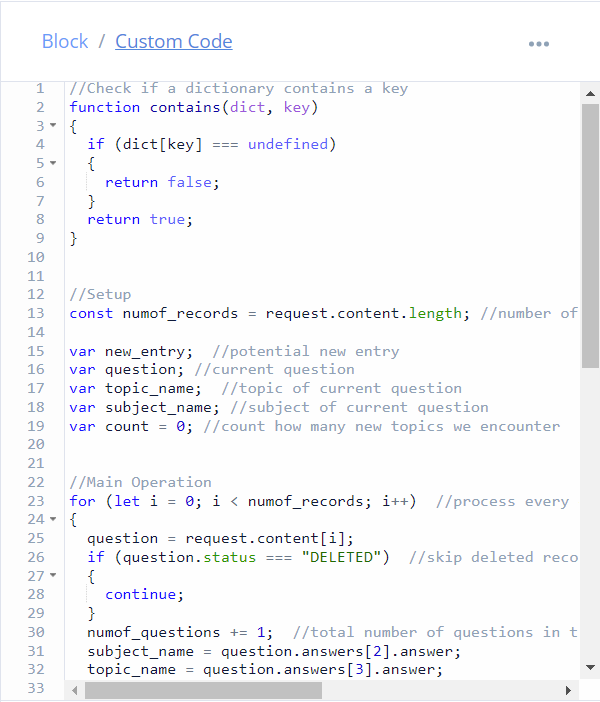
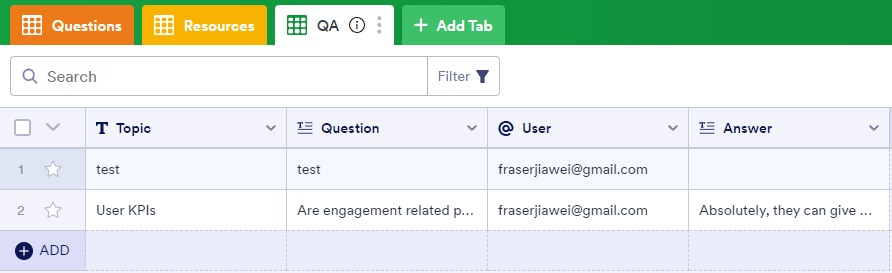
Q&A implementation overview:
Score implementation overview:

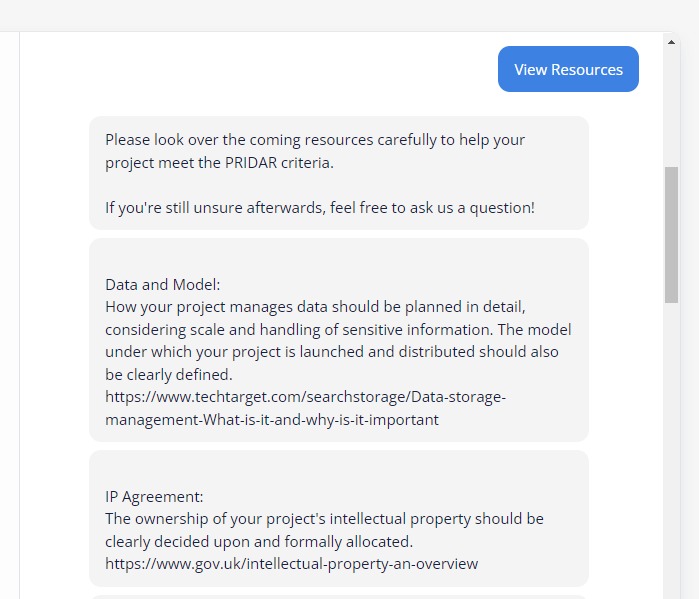
View Resources feature implementation:
If “View Resources” is selected, The resource for each topic is retrieved using a GET request to jotform which are then sorted based on topic and then listed to the user.
Telegram Bot Implementation Overview:
 Function name Function name |
Parameters | Functionality |
| launch | message | implements API calls to VoiceFlow for first message |
| sendMsg | message | implements API calls to VoiceFlow |
| start | message | forwards the payload extracted from the response to the user (only implemented when "/start" command is received) |
| handle_message | message | forwards the payload extracted from all responses to the user after first message |
The PRIDAR chatbot is implemented using Voiceflow and deployed as a telegram bot, which is implemented with a python backend to receive and send messages from telegram. The backend makes https requests to Voiceflow with the received messages using the acquired Voiceflow API key and extracts the response payload to forward back to telegram.
The python backend uses the “pyTelegramBotAPI” library together with a generated API key for the telegram bot to initialise a “telebot” instance which is used to handle all incoming messages from the user using two implemented message_handler().
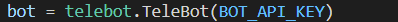
The first message_handler() is called when the “/start” command is received, which is implemented to call launch() and forwards the payload extracted from the response to the user.
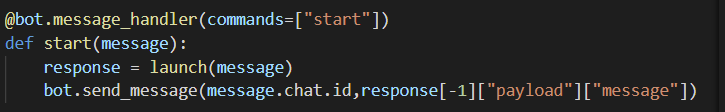
The second message_handler() is called on all other messages, which is implemented to call sendMsg(). The payload is then extracted from the response and forwarded to the user.
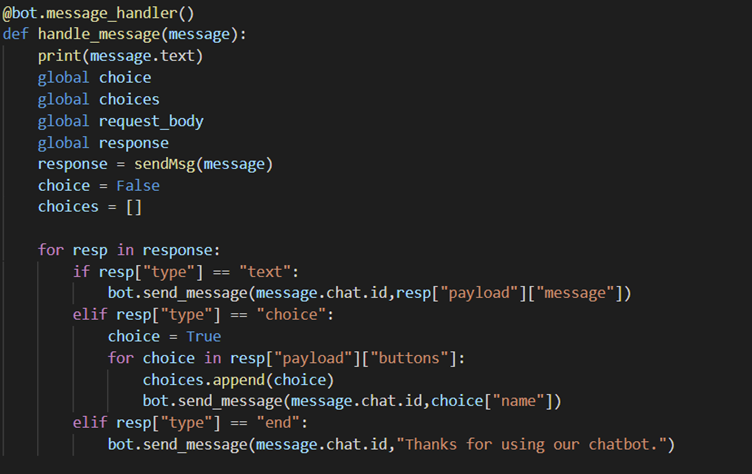
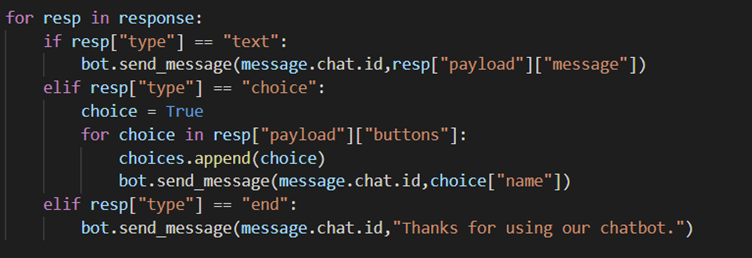
launch() and sendMsg() implements the API calls to Voiceflow using the message parameter and the generated API key for Voiceflow. Each API call is made with the appropriate type and the message as the payload. The endpoint used also contains the id attribute of the message which is unique to each user so that Voiceflow can track where each user’s state in its diagram flowchart and hence be able to respond with correct message.
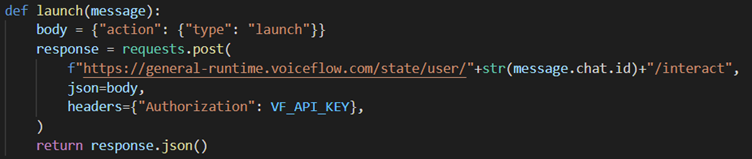
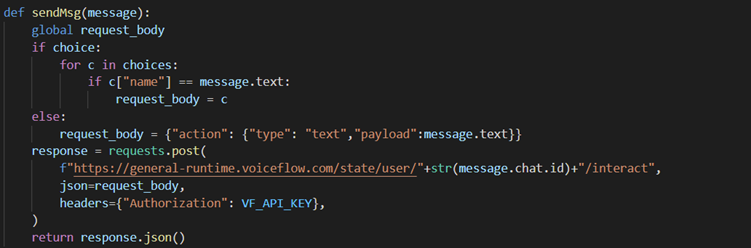
For each Voiceflow API response that requires a user reponse it is either of text or choice type. The backend uses a type flag to store the type of the latest response, if it is of choice type then all choices and its corresponding request body has to be stored for use in the next API call. When sendMsg() is called it checks the type flag, if it is set to text then the type is set to text and the payload set to the response from the user. If the flag is set to choice then the stored request body matching with the choice is used to make the API call to Voiceflow.