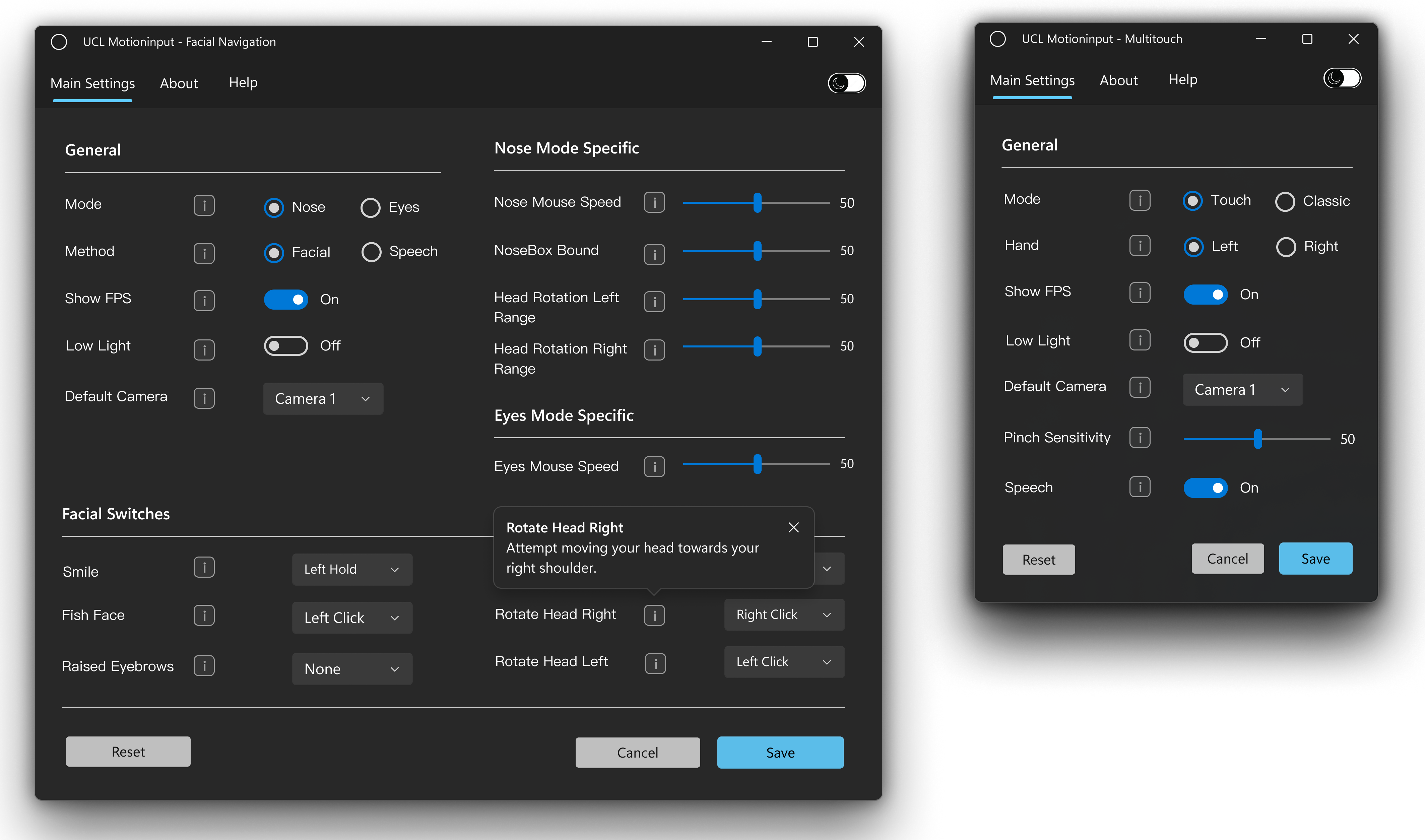
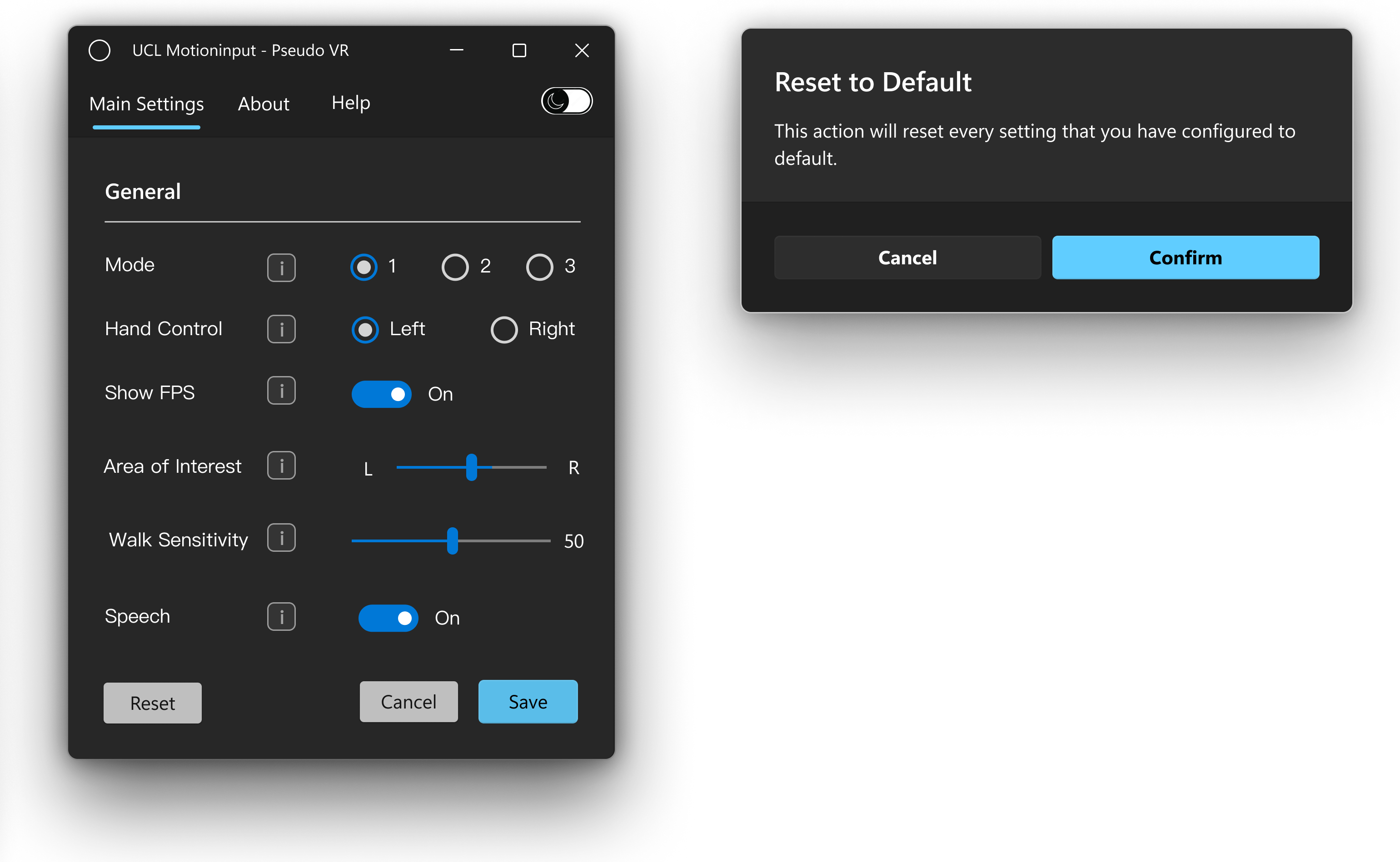
UI Design
1. Design Principles
Simplicity
Our focus is keeping design elements simple and intuitive to enhance the user's experience. A simple design allows users to quickly understand the function of an interface or application and reduce the learning curve. In turn, this improves the user's ability to complete tasks and achieve their goals. The simplicity principle is particularly relevant in today's fast-paced world where users expect instant gratification and ease of use.
Consistency
Our goal is maintaining a consistent design across all elements of an interface or application. A consistent design ensures that users can easily navigate and understand the interface without confusion. It also makes it easier for users to learn how to use new features or functions because they are already familiar with the design patterns. Consistency is essential in creating a cohesive user experience and building user trust.
User Centricity
User centricity is a design principle that focuses on designing products and services that are centered around the needs and preferences of the end user. This principle emphasizes the importance of understanding the user's goals, motivations, and behaviors when designing an interface or application. User-centric design ensures that the product or service is relevant, meaningful, and easy to use. User centricity involves conducting user research, analyzing user feedback, and incorporating user preferences into the design process.
Feedback
Feedback is a design principle that refers to providing users with feedback on their actions within an interface or application. Feedback can be provided through visual cues, sounds, or other sensory inputs. Feedback helps users understand how the interface or application responds to their actions, reducing uncertainty and improving the user experience. It also encourages users to explore the interface or application and learn more about its functionality.
Reduce Cognitive Load
Reduce cognitive load is a design principle that aims to reduce the mental effort required to use an interface or application. Cognitive load refers to the amount of mental processing power required to complete a task. Reducing cognitive load can be achieved through design techniques such as simplifying navigation menus, using clear and concise language, and minimizing visual distractions. By reducing cognitive load, users can focus on completing tasks and achieving their goals, rather than being distracted by unnecessary information or confusing interfaces.
References:
[1] Interaction Design Foundation. (n.d.). Simplicity in Design. Retrieved from https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/topics/simplicity
[2] Smashing Magazine. (2019). Consistency in Design: Why It's Important and How to Achieve It. Retrieved from https://www.smashingmagazine.com/2019/03/consistency-design-importance-achieve/
3] Nielsen Norman Group. (n.d.). User-Centered Design Basics. Retrieved from https://www.nngroup.com/articles/definition-user-centered-design/
2. Sketches
Once we understood what our users wanted, we started coming up with design ideas. We brainstormed a lot and used feedback from users to improve the best ideas. Then we made several prototypes at the same time based on the best ideas we had.
Sketch 1
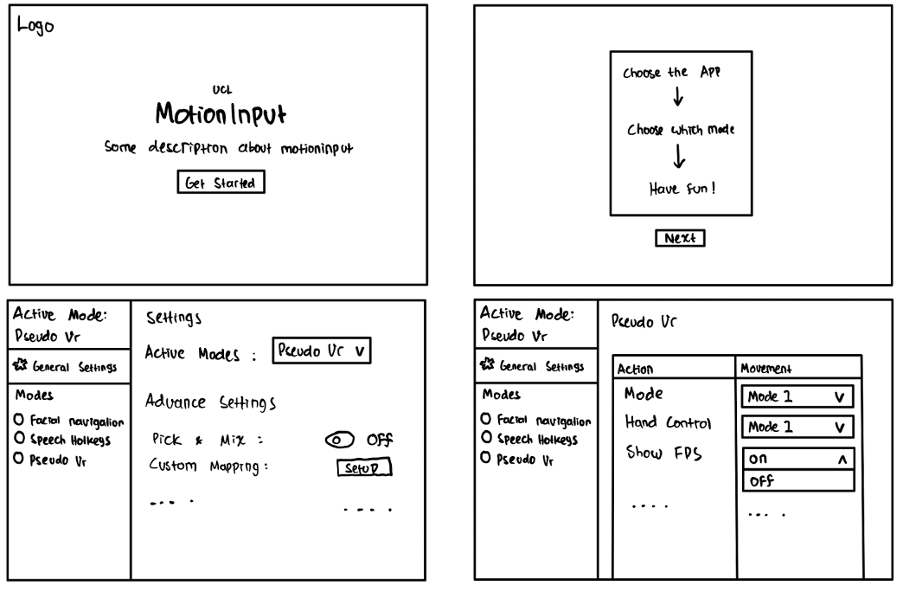
Sketch 2
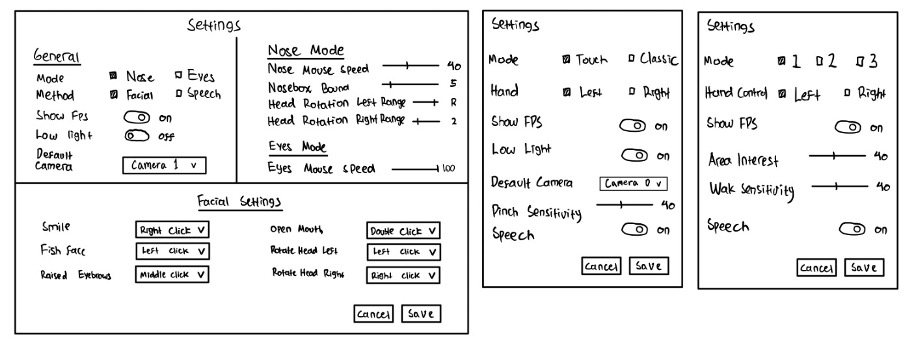
3. Initial Prototype
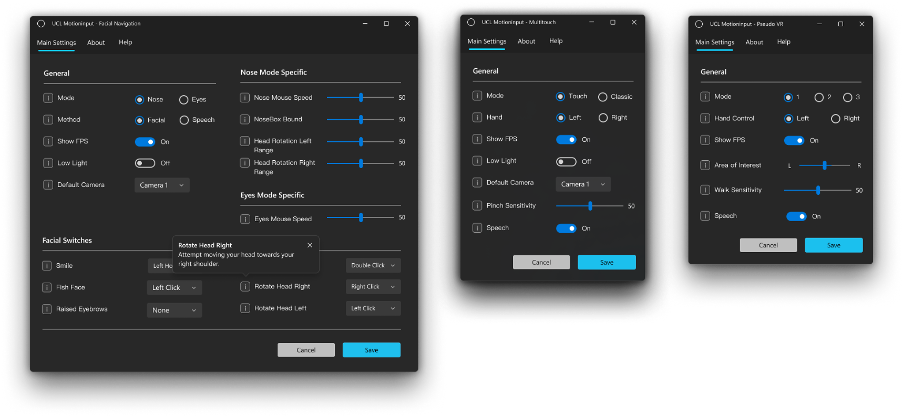
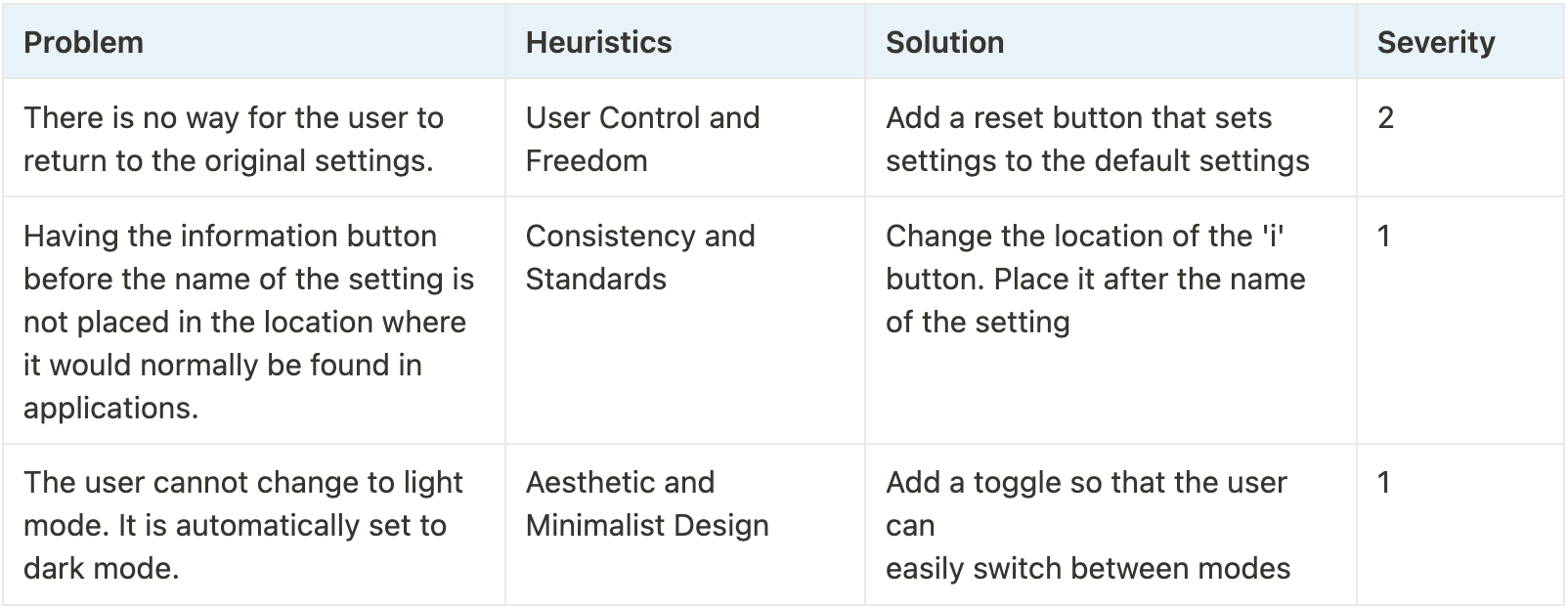
4. Heuristic Evaluation
Once we made some pictures and simple models of our ideas, we checked to see if they worked well for users. We did this in two ways. First, we asked other people to look at our designs and give us feedback. We also looked at our designs ourselves to see what could be improved.
5. Revised Prototype
After we finished evaluating our design, we went through a process of making it better. We did this by looking at what worked well and what needed improvement. Then we made changes to our prototype based on this feedback, with the goal of creating a more user-friendly and effective design.