Description
After merging data records to common categorizations, and clearing the data of obvious errors, to avoid potential reporting bias and other errors, a slicing algorithm was applied to cut out the less reliable part.
Observation
By going through the data distribution plots, we have the following observations:
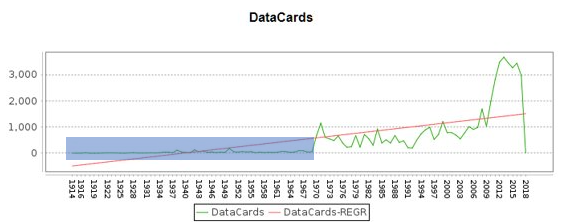
- The number of data records varies from country to country, sometimes by orders of magnitude.
- The distribution of records are not even through time.
Examples:
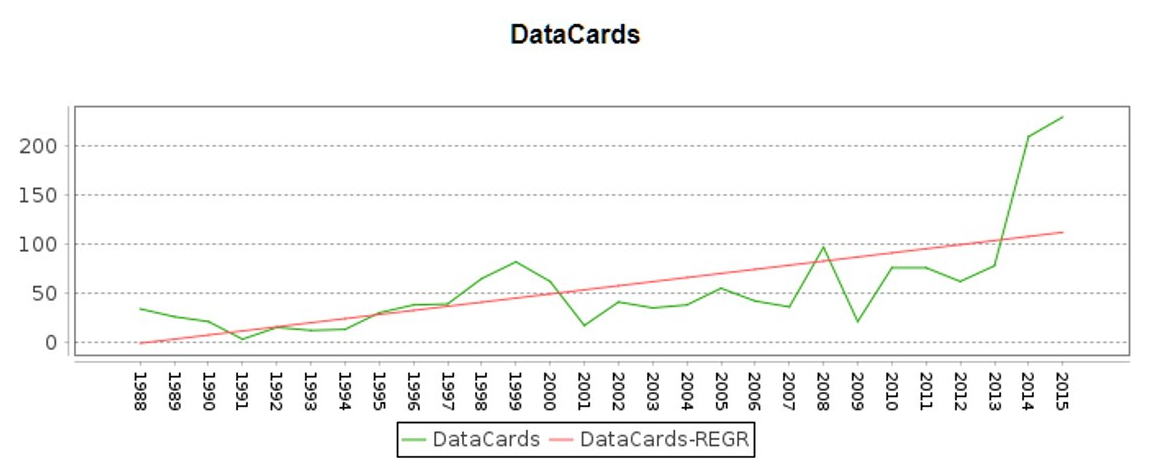
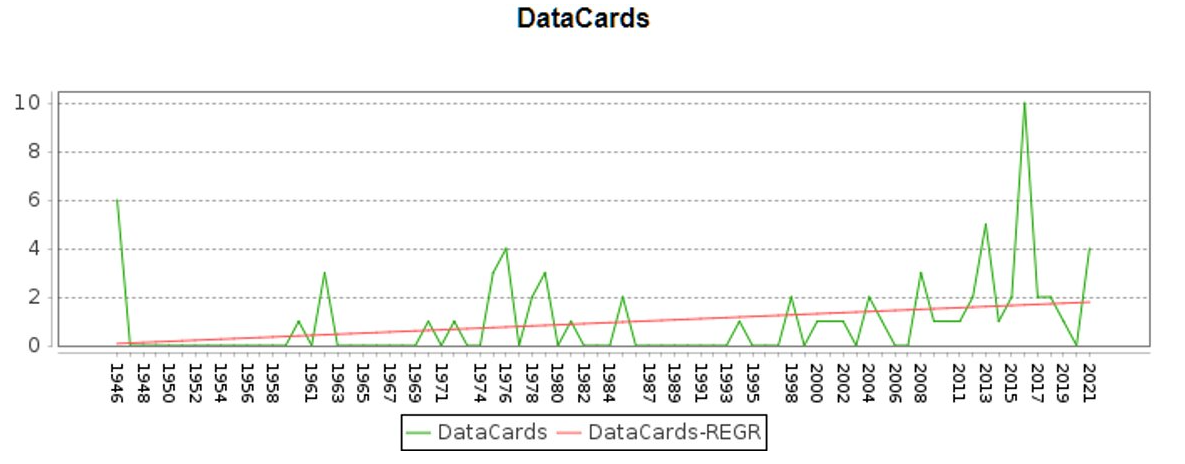
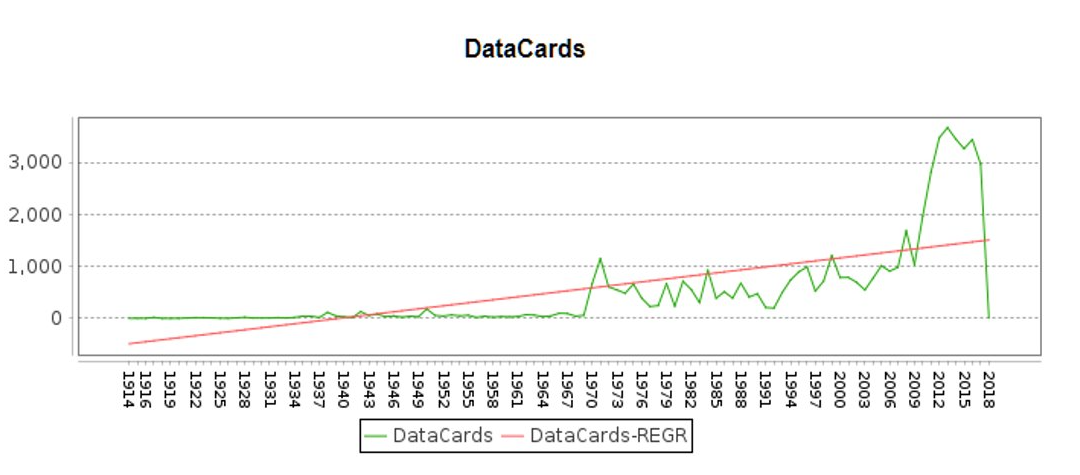
Assumption
The slicing algorithm is designed based on the following assumptions:
- The reliability and accuracy of every country increase through time.
- Hazards tend to be more frequently due to the global warming and climate change.
Algorithms
Evaluation
Hard to define abnormal threshold. May violate assumption one. Therefore it is not deployed.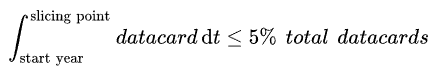
Fig.1. The first 5% records (in blue) were discarded
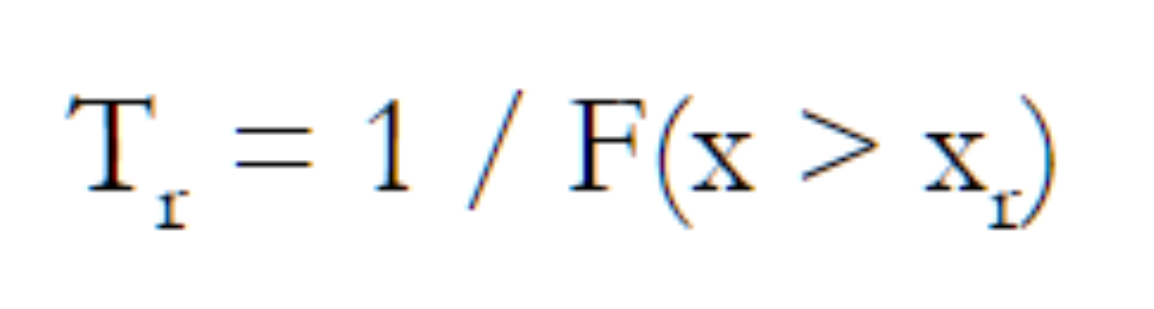 (1.1)
(1.1)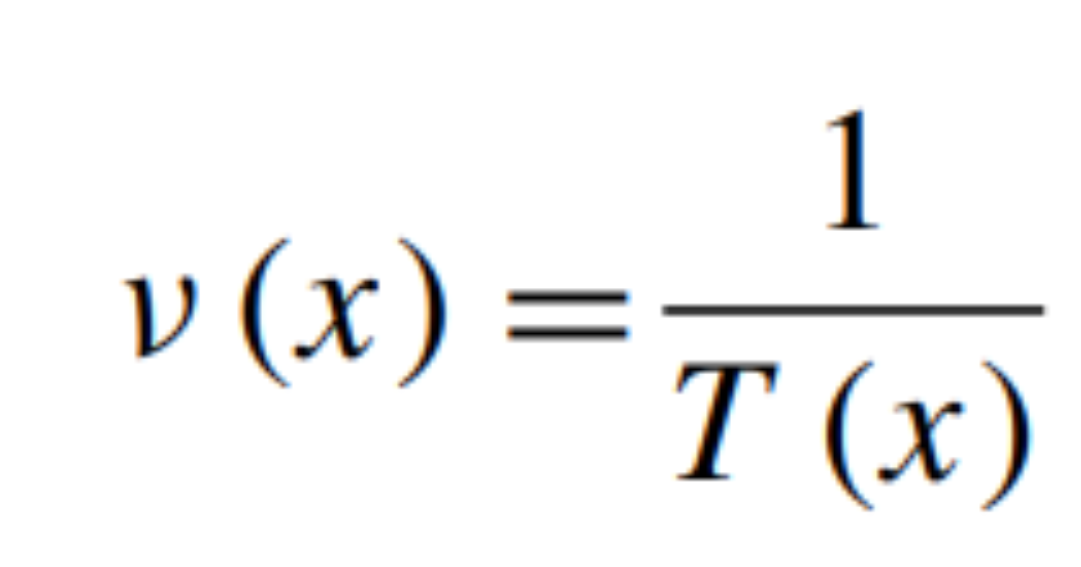 (1.2)
(1.2)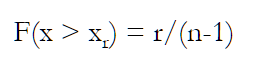 (1.3)
(1.3)