Implementation
Overview
Backend
- Flask: Core web framework that handles API endpoints, routing, and business logic
- SQLAlchemy: Database interaction layer for booking, user, and timeslot management
- Flask-Mail: Email sending library for sending booking confirmations
- AzureOpenAI: Provides AI model to assist users
Frontend
- React: Component-based UI library
- TailwindCSS: CSS framework for styling components
- Web Speech API: Native browser API for speech recognition and synthesis
The following sections detail the implementation of the main features of our project:
We chose to discuss these features as they serve the core logic of our application, and involve both frontend and backend components.
Scheduling
Create Booking
To allow for the creation of bookings, we implement a POST route in the backend at the
/api/bookings/create_booking endpoint. This endpoint receives user details and booking
information in
the request body. The route is responsible for creating the booking, associated timeslots (if they don't
exist), associated user (if they don't exist), saving these to the database, and finally, if successful,
sending an email confirmation to the user.
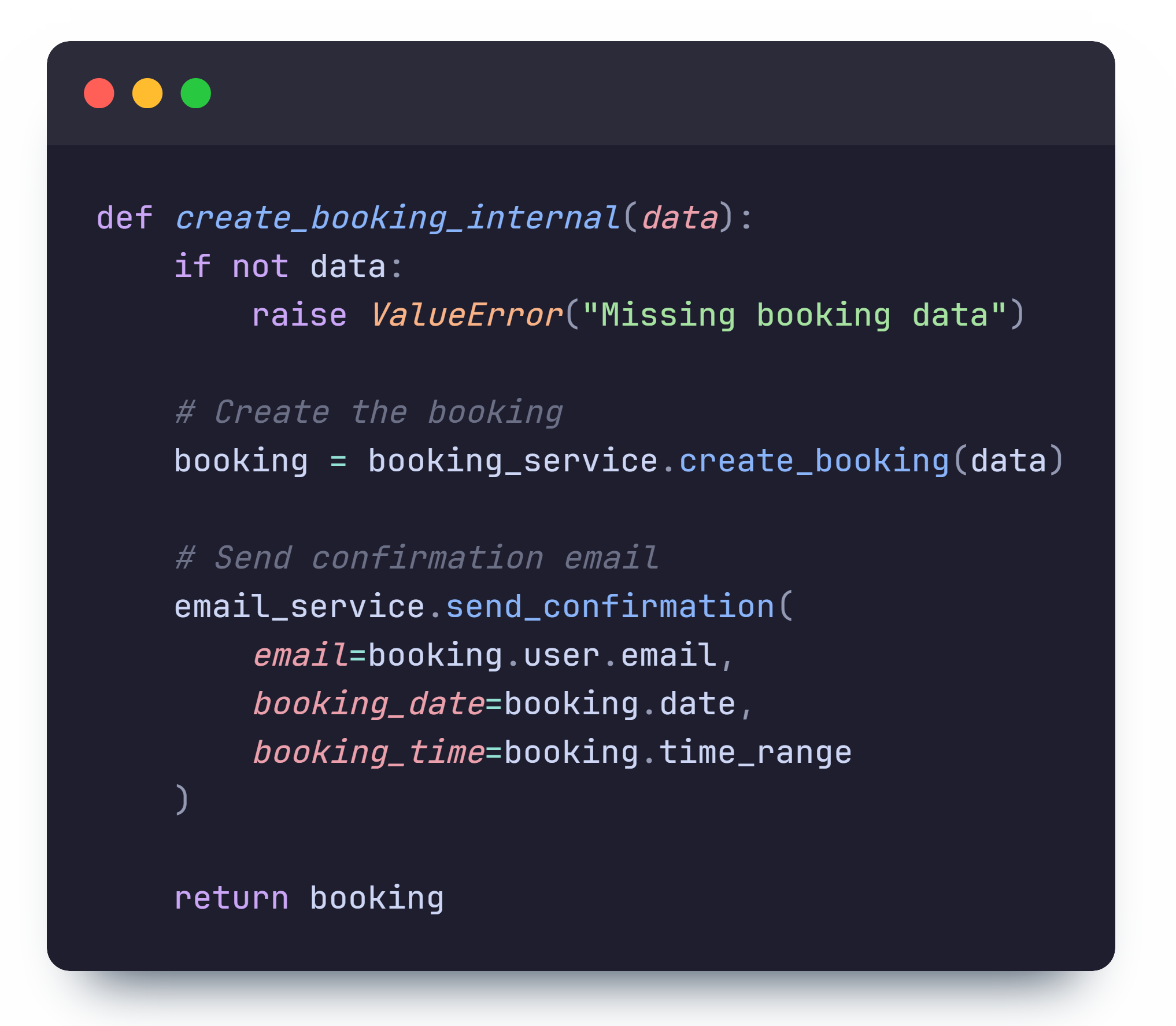
The route method itself contains a call to the internal method above and handles errors. The internal method receives user details and handles the booking creation process through the following steps:
- Create a booking (by calling the abstracted method in
BookingService) - Send a confirmation email if successful (through
EmailService) - Return the created Booking object
While much of the logic is abstracted and placed in respective services such as
TimeslotService and UserService, the core booking creation logic is
contained within the create_booking method in the BookingService class.
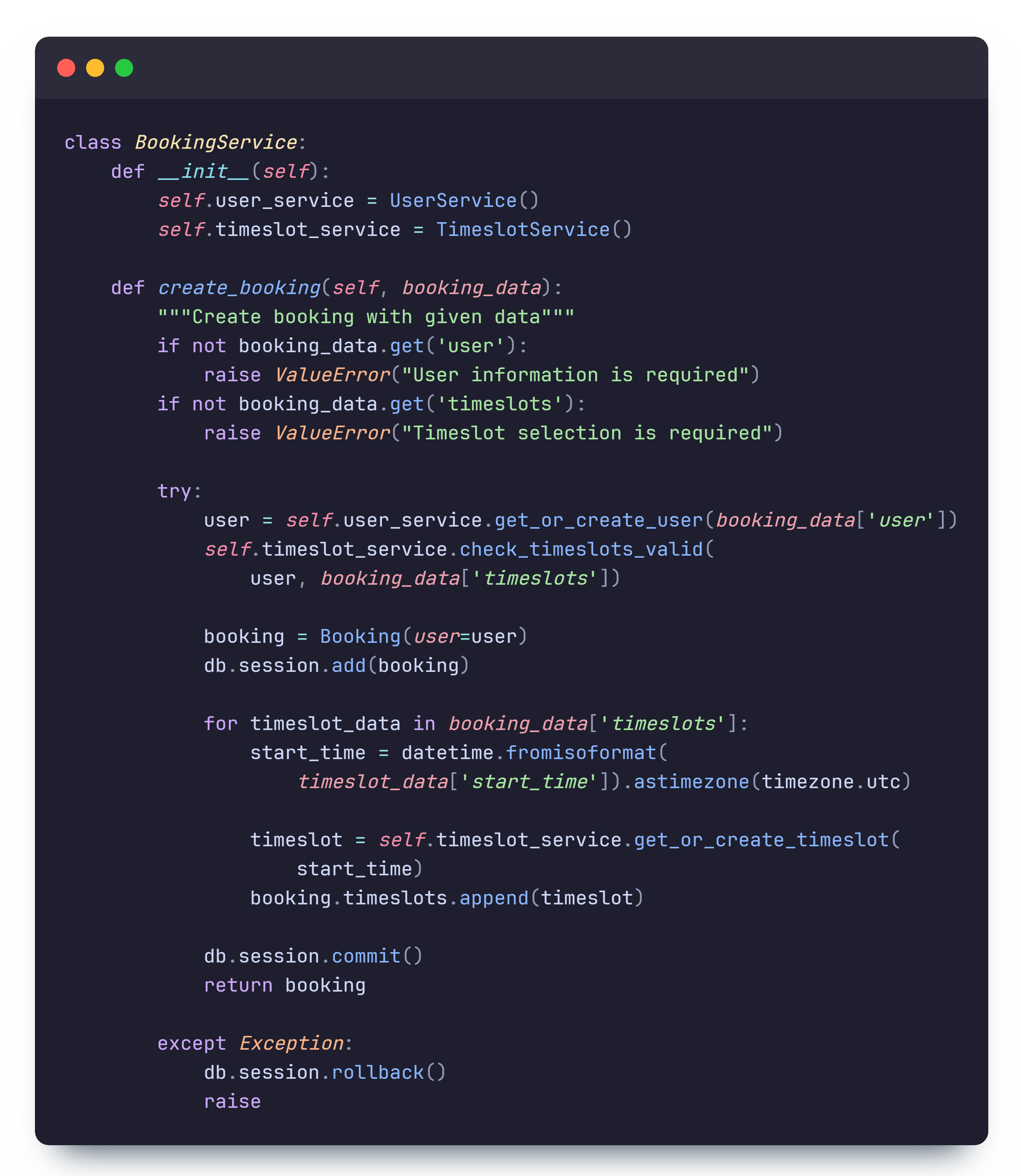
The method works by first calling get_or_create_user from the UserService to
retrieve the user from the database or create a new one if they don't exist (identified by email).
It then calls check_timeslots_valid from the TimeslotService to ensure that
timeslots are not overlapping, are within opening hours, are scheduled in the future, are consecutive, and
are
available.
After validation, the booking is created and added to the database. Each timeslot is then
created/retrieved and
associated with the booking. At any point, if an error occurs, the booking is rolled back and the error
is propagated to the route handler.
Fetching Availabilities
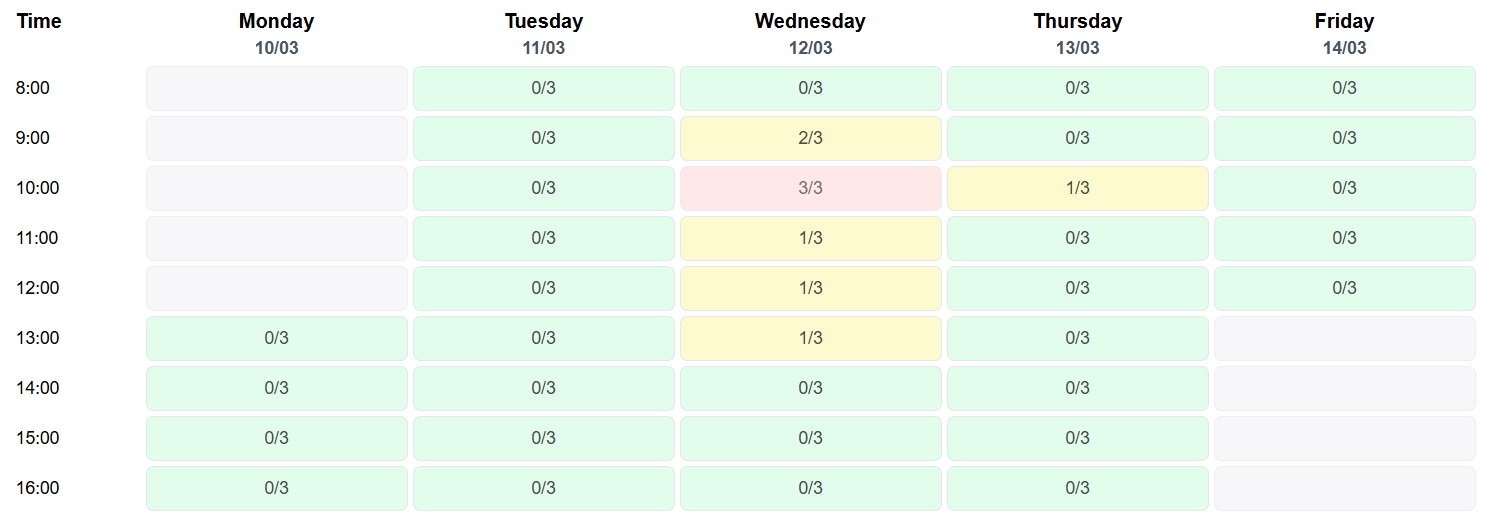
The booking system implements a time slot availability feature that lets users see the number of people that have a booking for each timeslot in the frontend. The purpose of this feature is to provide users with information about the availability the café at different times of the day, allowing them to have more context when making a booking.
Frontend Implementation
The frontend of the availability feature is implemented within the TimeSlotGrid component,
which is responsible for rendering the time slot cells. When the component is mounted, it fetches the
availability data from the backend with a useEffect hook and updates the state with the
fetched data.
The availability data is then used to render the time slot cells with the appropriate styling based on
the
number of bookings for each time slot, e.g. green for high availability, yellow for medium availability,
and red for full.
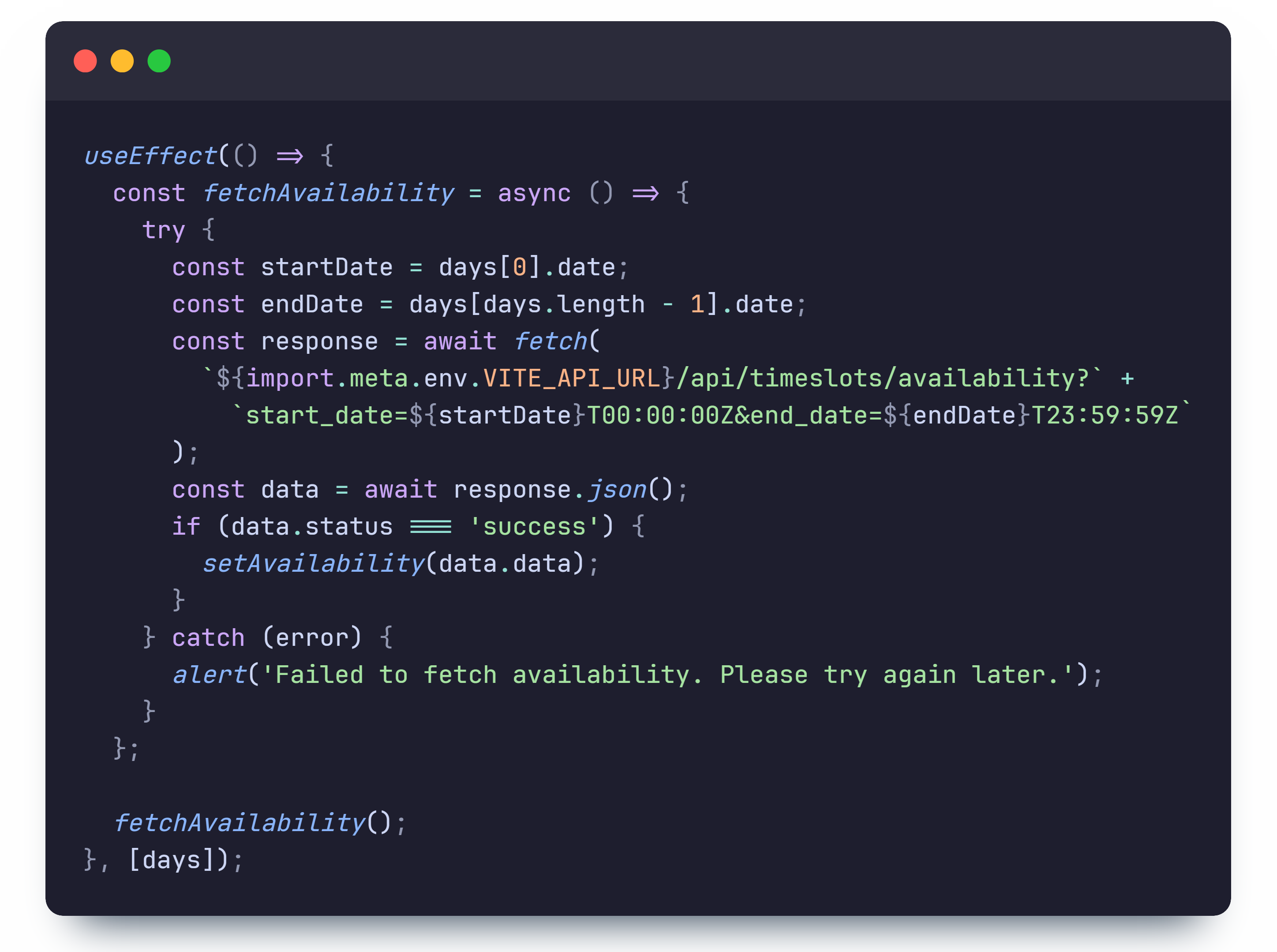
The fetchAvailability function sends a GET request to the backend
/api/timeslots/availability?start_date={start_date}&end_date={end_date} endpoint to fetch
the availability data for the specified date range. This route then returns JSON data containing the
number of bookings for each time slot, which is then used to update the state.
Backend Implementation
The backend implementation of get_availability is as follows:

This GET endpoint queries the database for time slots within the specified date range and
returns JSON with the booking count for each start time. Note that start times are unique for timeslots
and
booking_count is a property in the timeslot model which represents the number
of
bookings it is associated with.
By separating the route handler logic into internal functions (like
get_availability_internal), we
achieve two
important benefits:
- The AI assistant can directly call these internal functions without making HTTP requests, which it cannot do in production due to security restrictions
- This separation improves testability and code reuse across different parts of the application
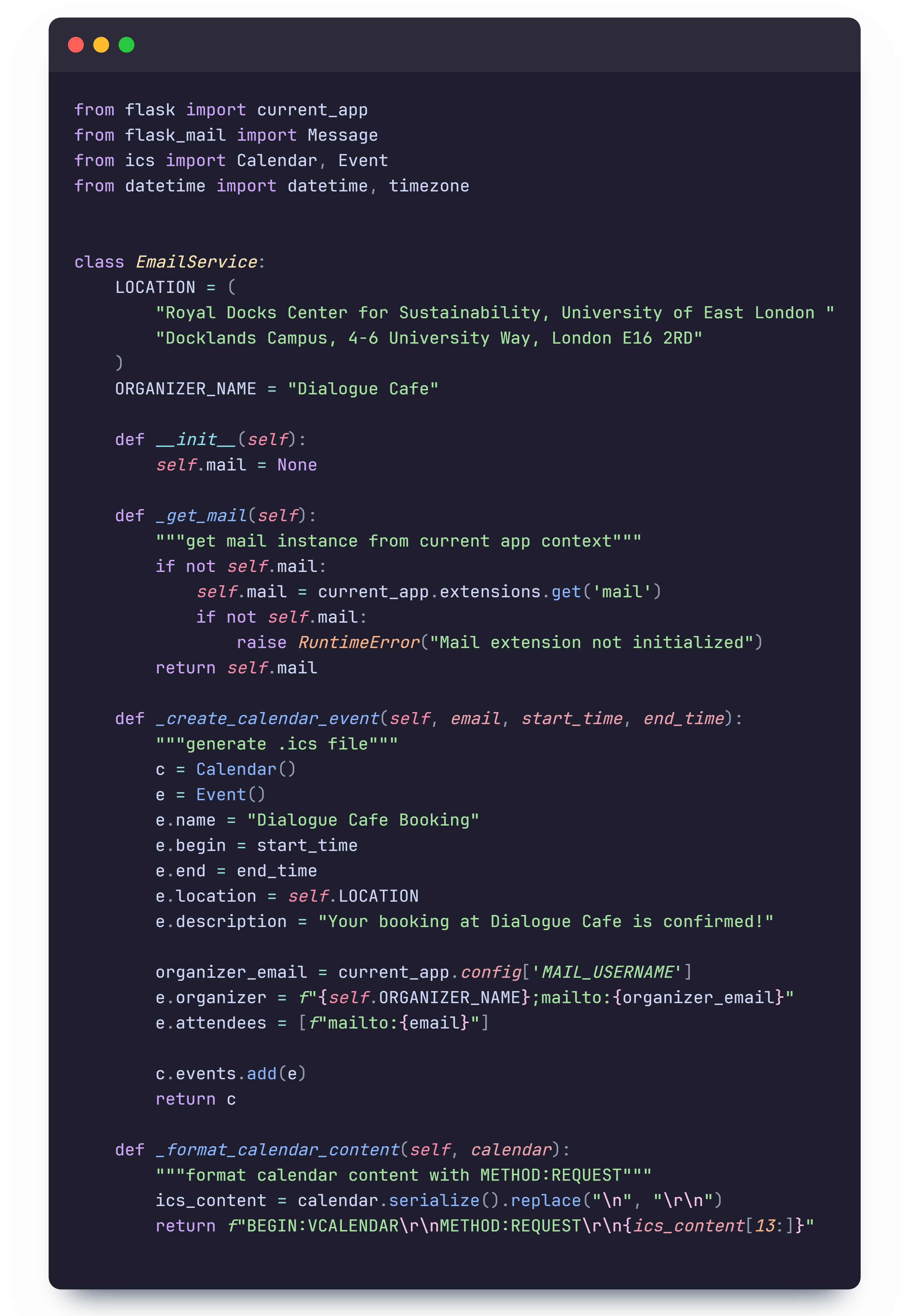
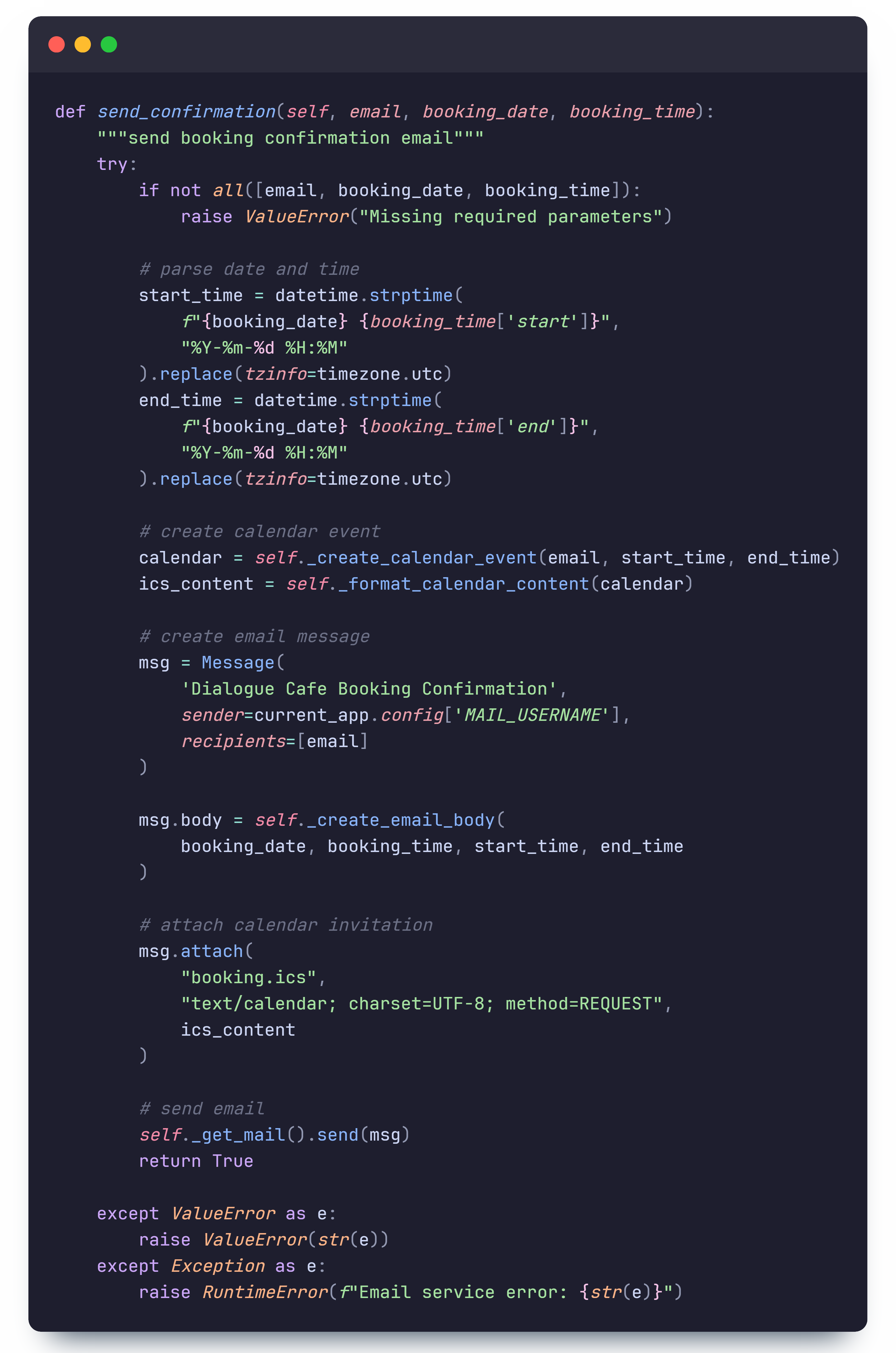
Email Confirmation
The email confirmation system is implemented using Flask-Mail. This package was chosen over alternatives because our backend is developed with Flask, ensuring compatibility and a seamless integration process.
When a user successfully books a session, an automated email is sent with the following information:
- The booking date and time
- Location details
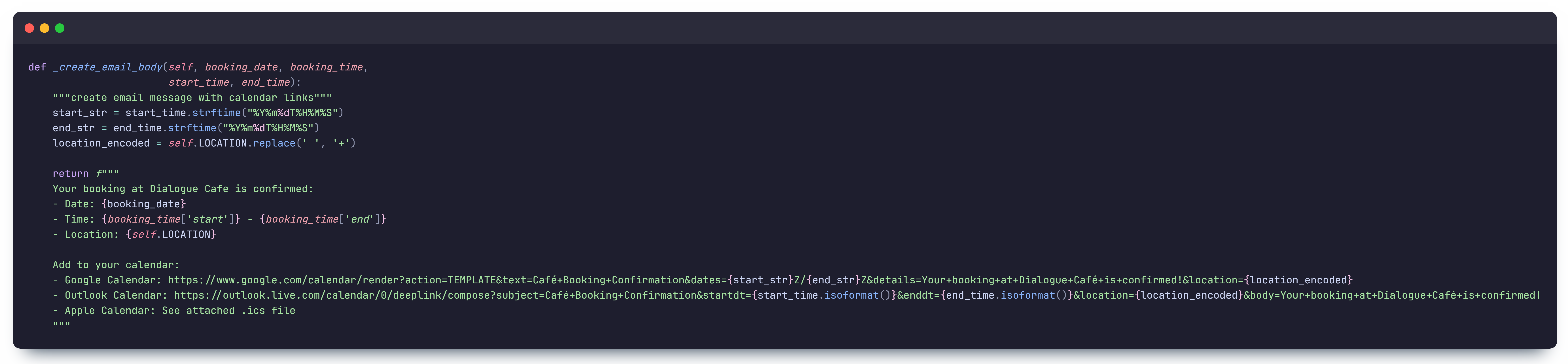
- Links to add the booking to Google, Outlook, or Apple Calendar
- An attached
.icsfile for easy calendar integration
The email confirmation process involves:
- Parsing the booking date and time into UTC format.
- Generating a
.icsfile using theicsPython package. - Constructing an email with the booking summary, calendar links, and an attachment.
- Sending the email via Flask-Mail using an SMTP server.
AI Assistant
The AI assistant is developed using Azure OpenAI services. This approach was selected due to the robust integration capabilities Azure provides, along with access to the latest GPT models for generating high-quality responses. We used AI Assistants over chat completions as they provide tools for session management such as threads which allow us to retain context. They also have better support for function calling capabilities, which we use so that the AI can interact with our backend services and perform actions for users.
Process Flow
User Input Capture
Frontend interface captures user queries through text or voice input
Azure OpenAI Processing
Queries are processed by GPT models for contextual understanding
Response Generation
AI returns response based on the user query and its contextual understanding
Real-time Delivery
Responses are displayed in the user interface
Implementation Details
Backend Integration
Azure OpenAI GPT models integrated through Python's openai library for robust processing
Frontend Interface
React components for real-time chat interactions and voice input handling
Knowledge Base
Integration of Dialogue Cafe FAQ, BSL videos, and backend function calls to enhance response quality
Security
Secure API key management through an Azure Key Vault and request validation through environment variables
Backend Implementation
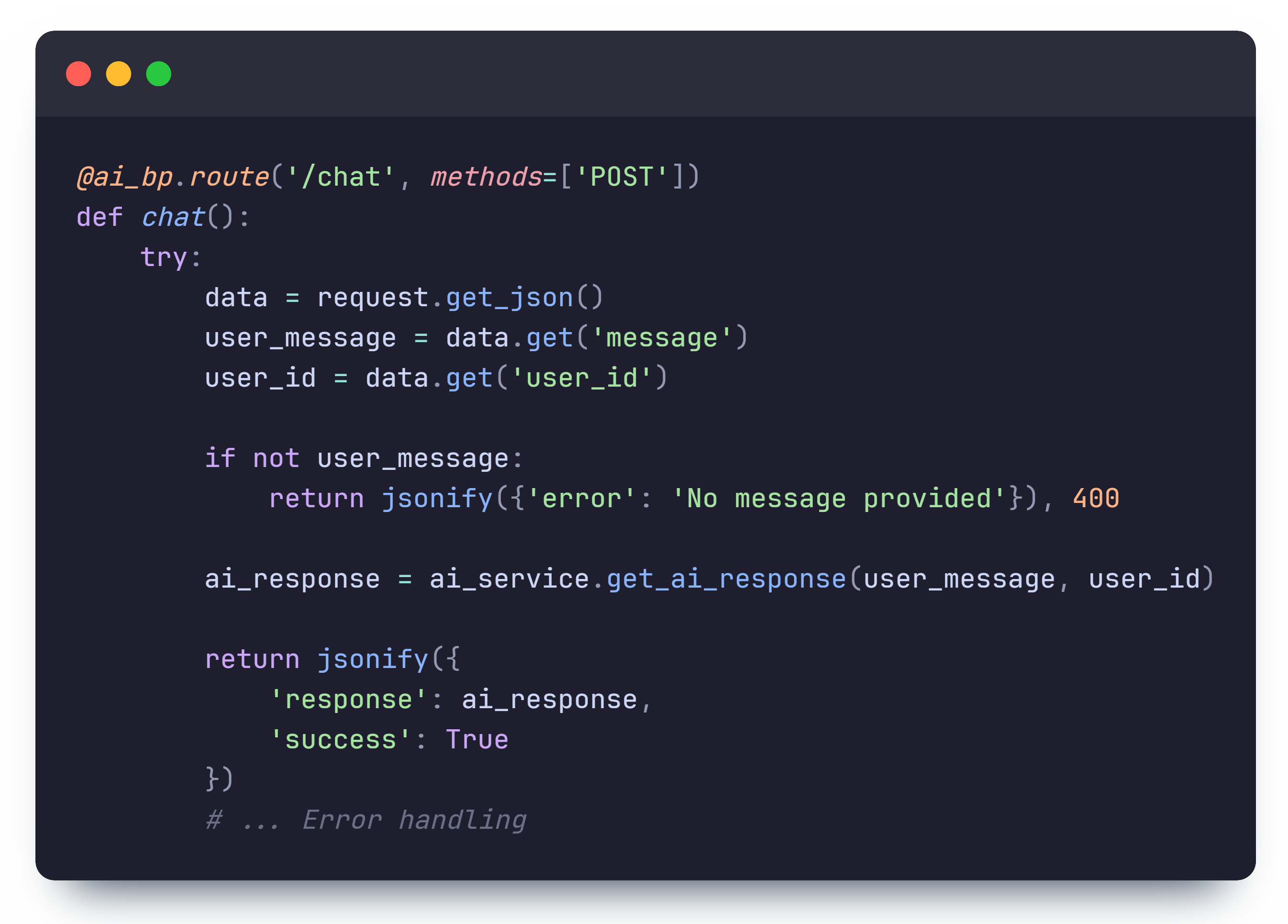
When a user sends a message in the frontend, a POST request is made to the
/api/ai/chat route which takes the message and a user ID as input.
The user ID is generated in the frontend upon visiting the site with const [userId] = useState(() => crypto.randomUUID());
. This allows the backend to identify the user and maintain context across multiple messages
during a session.
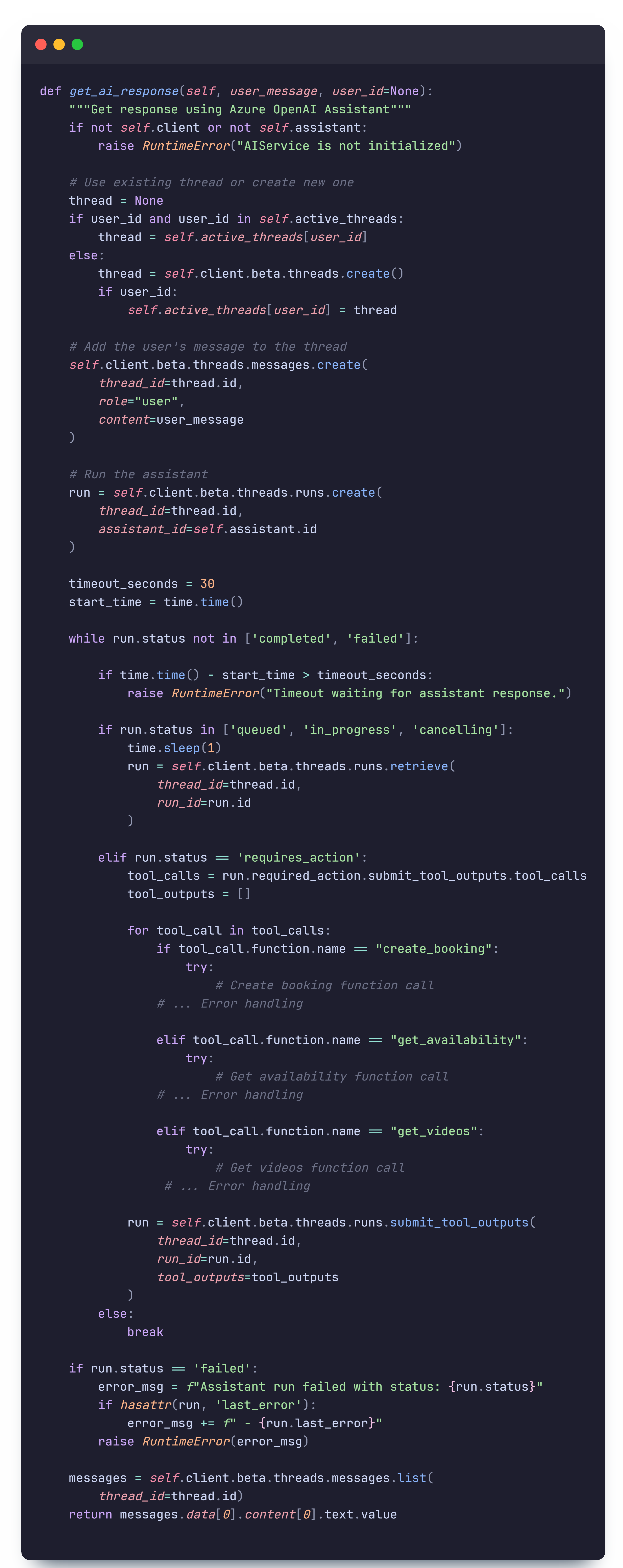
This route handler then calls the get_ai_response function which processes the user message
with our custom AI model and
returns a response.
This method seem quite long, but can be broken down into the following steps:
- Connects the user to a thread based on their
user_id, (threads manage context, so this allows users to retain context throughout messages) - Adds the user message to the thread
- Creates a 'run' to process all methods in the thread
- Performs required actions function calls
- If successful, returns the response
Now within step 4. to perform the required actions there is additonal complexity which is contained in the while loop. Essentially, the assistant can have different states. While the state is not 'completed' or 'failed', the assistant runs in a loop of actions. When the state is 'requires_action', this means that the assistant has realised that it needs to perform one of its function calls.
The AI can make three different function calls: create_booking,
get_availability, and get_videos. Create booking calls the internal create
booking method to
create a booking, get availability calls the internal get availability method to get the availability of
time slots, and get videos
searches a dictionary of BSL videos and displays text in the format [VIDEO:type:video_name], which the
frontend converts
into the the corresponding embedded video. The AI is provided information on how to process these calls
in its instructions, and given configurations for the parameters of each function.
Key Features
Voice Input
Speech-to-text for natural interaction
Booking Assistance
Guided booking process
FAQ Support
Instant answers to common queries
BSL Information
Sign language resources