System Design
System Architecture Overview
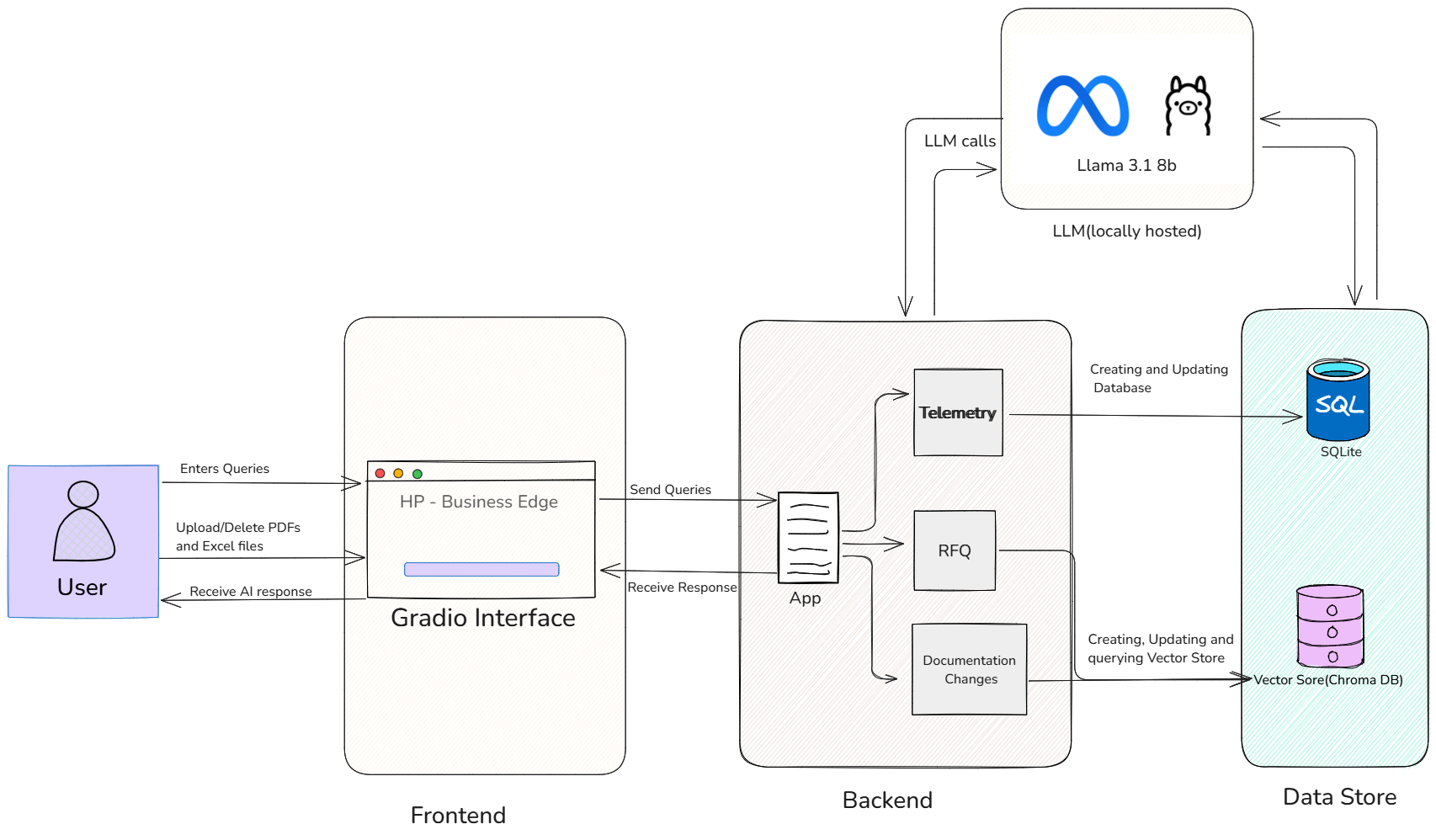
Figure 1: Overall system architecture diagram
The system architecture is structured to provide a user-friendly experience, leveraging a Large Language Model (LLM) and supporting data storage for intelligent information processing.
User Interaction Layer (Frontend)
The Gradio Interface forms the user's primary interaction point. Gradio is an open-source Python library used to create interactive web applications. In this system, it:
- Provides an interface for users to input queries
- Handles uploading/deleting PDF and Excel files
- Displays "HP - Business Edge"
- Presents AI-generated responses
Backend Processing and Logic
The App (Backend) manages core system operations:
- Receives queries from Gradio and routes them to the 3 different systems
- Orchestrates interaction between the LLM, SQL database, and vector store
- Implements Telemetry for the AI SQL Agent
- Handles RFQ (Request for Quotation) and Documentation Changes using Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
Large Language Model (LLM)
The LLM (Locally Hosted Llama 3.1 8b) provides AI functionality:
- Generates natural language responses
- Assists with SQL query handling
- Powers information retrieval for RFQ and Documentation Changes
Data Storage and Retrieval
The Data Store comprises:
- SQL (SQLite): A relational database for structured data, used for database management and SQL query execution
- Vector Store (Chroma DB): A vector database for storing embeddings, crucial for semantic search in RAG-based RFQ and Documentation Change processing
Site Map
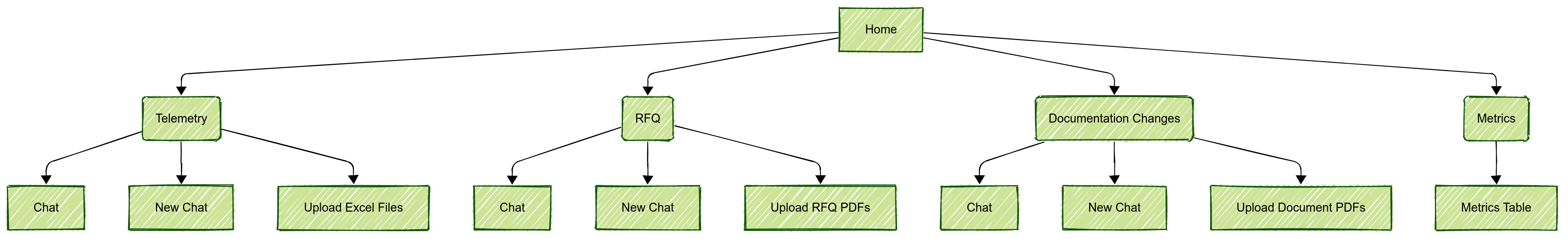
Figure 2: Site Map
Starting Point: The user begins on the Home page.
Accessing Core Functionalities: From the Home page, the user can choose to navigate to one of four main sections:
Telemetry
RFQ
Documentation Changes
Metrics
Within Telemetry, RFQ, and Documentation Changes: In each of these sections, the user has three primary options:
- Chat: To engage in an existing conversation
- New Chat: To start a new conversation thread
- Upload [Specific File Type]: To upload files relevant to that section (Excel files for Telemetry, RFQ PDFs for RFQ, and Document PDFs for Documentation Changes)
Accessing Metrics: By clicking on Metrics from the Home page, the user will be taken directly to the Metrics Table for viewing and analyzing data.
Design Patterns
Composite Pattern
Used for representing hierarchical structures where individual objects and compositions of objects are treated uniformly.
Template Method Pattern
Defines the skeleton of an algorithm in the superclass but lets subclasses override specific steps of the algorithm without changing its structure.
Model-View-Controller (MVC)
Separates application logic from user interface, improving maintainability and testability.
Mediator Pattern
Defines an object that encapsulates how a set of objects interact. Promotes loose coupling by keeping objects from referring to each other explicitly.
Repository Pattern
Abstracts the data access layer, providing a clean interface for data retrieval and manipulation.
Strategy Pattern
Defines a family of algorithms, encapsulates each one, and makes them interchangeable. Lets the algorithm vary independently from clients that use it.
Adapter Pattern
Allows interfaces of incompatible classes to work together by converting the interface of a class into another interface clients expect.
Observer Pattern
Defines a one-to-many dependency between objects so that when one object changes state, all its dependents are notified and updated automatically.